I. What is a Mineral?
A. Naturally Occurring
B. Inorganic
C. Solid
D. Definite Chemical Composition and Shape
E. Crystal -Atoms arranged in a repeating pattern.
II. Identifying Minerals
A. Color B. Luster
C. Hardness (Mohs) Pg. 69
D. Streak- Mark left on unglazed porcelain tile.
E. Density- Mass per unit Volume (g/cm3)
F. Crystal Shape-pg. 62
G. Cleavage- Breaks leaving a smooth surface
& Fracture- Breaks leaving rough edges
III. Uses of Minerals
Example: Diamond, Emeralds
B. Ores- Minerals that are mined for a profit.
Examples: Metals, Sulfur
C. Asbestos- Fine fiber used in insulation and fire resistant materials. Fibers get in lung and cause lung cancer.
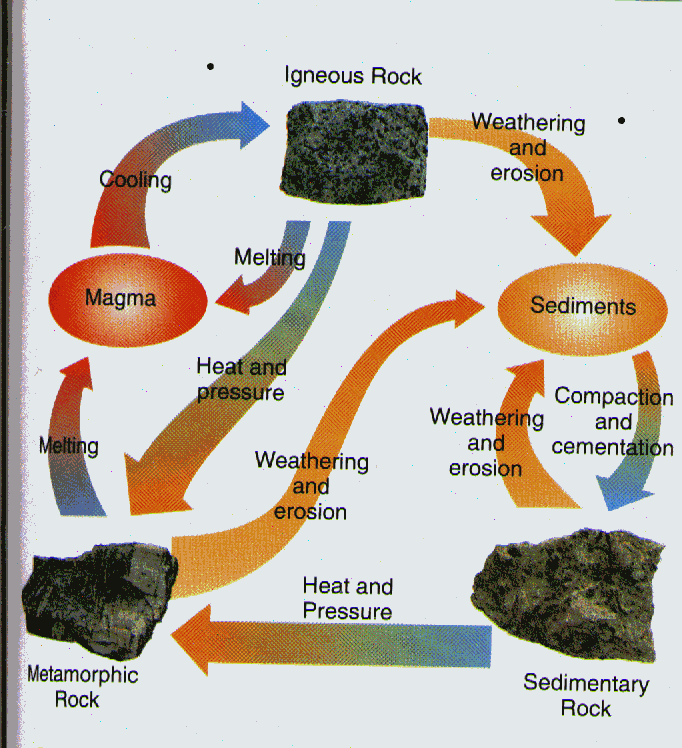
IV. The Rock Cycle

V. Igneous Rock (From Fire)
A. Melting
1. Temperature- 1400 C (2550 F)
2. Radioactive- Elements in surrounding rocks produce thermal energy
B. Classification
1. Where it's formed
a. Intrusive (Magma) - inside the earth
b. Extrusive (Lava)- outside the earth
2. Color
a. Dark-Basaltic
b. Light-Granite
3. Composition
a. Fast cooling, small Grains
b. Slow cooling, large Grains
VI. Metamorphic Rock
A. Heat & Pressure- granite is put under pressure
B. Classification
1. Foliated (Layers)- grains flatten and line up in parallel bands.
2. Nonfoliated (No layers)- grains rearrange but don't form bands.
VII. Sedimentary Rock (to Settle)
C. Classification
1. Clastic (Broken)- made from fragments of plants, animals and other rocks.
2. Chemical (Evaporates)- form from minerals dissolved in a solution.
3. Organic (Once Living)- made from remains from once-living organisms.