Chapter 15- Volcanoes
Ex. Iceland.

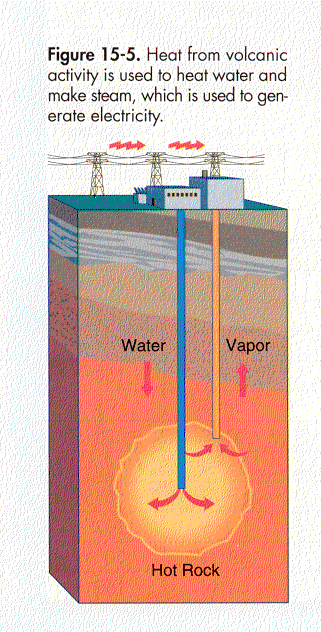
A. Electricity from G.E
. - Heat from magma can be used to heat water and produce steam. The steam is pressurized and spins generators that make electricity. Figure 15.5B. Problems with G.E.-
2.
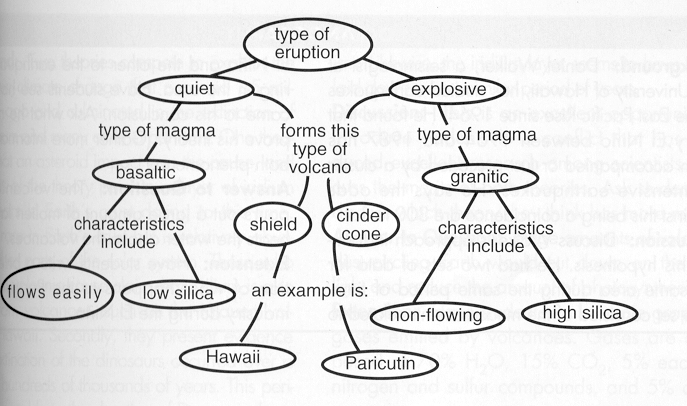
Quiet- The gas escapes before it reaches the surface and the magma is Basaltic and very fluid.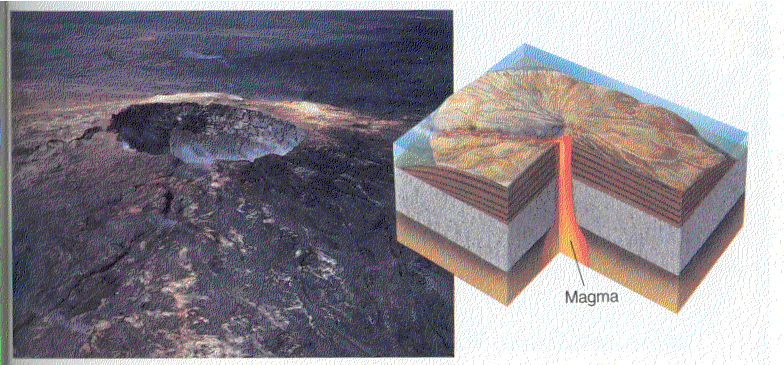
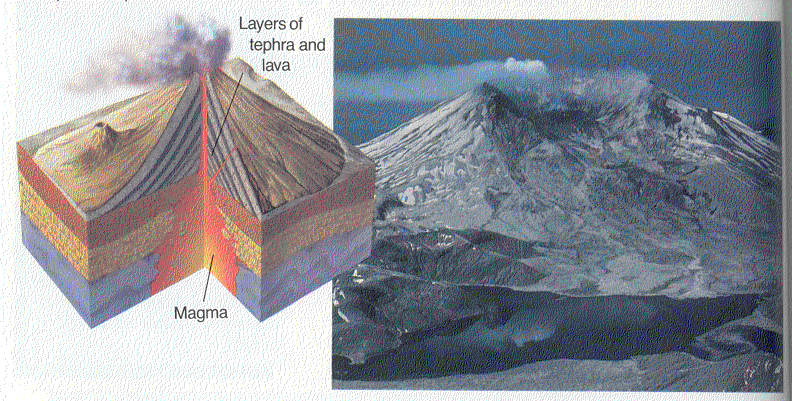
Explosive eruptions throw lava high in the air. When this lava cools it is called Tephra Cinder-cone volcanoes are created when Tephra falls to earth and piles up. Figure 15.9